
OR
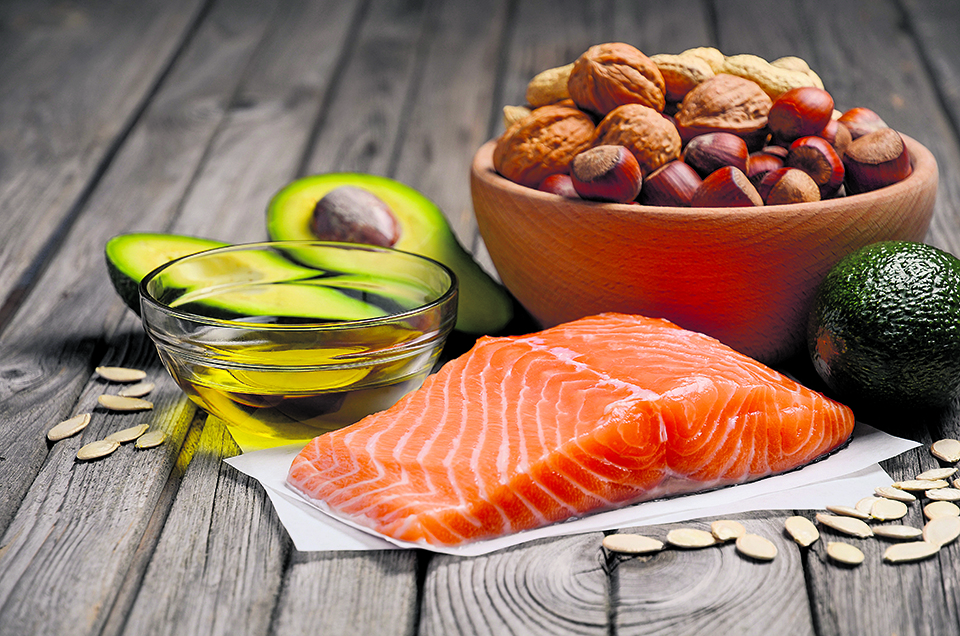

All of us have heard or read about the benefits of Omega-3 Fatty Acids, a subgroup of Essential Fatty Acids (EFA). They have powerful health effects on the brain and the body. However, they, along with Omega-6 Fatty Acids, cannot be synthesized in the human body and thus one has to obtain it from their diets. There are three vital Omega-3 Fatty Acids and they are Alpha Linolenic Acid (ALA), Eicosapentaenoic Acid (EPA) and Docosahexaenoic Acid (DHA). These components help in raising High density Lipoproteins (HDL) or the good cholesterol in the blood.
Sources of Omega-3 Fatty Acids
Omega-3 Fatty Acids can be obtained from animal sources like seafood, fish, and fish oil. Although fish is a dietary source of Omega-3 Fatty Acids, fish do not synthesize them; they obtain them from the microalgae or plankton in their diets. Fish oil contains 40% Omega-3 Fatty Acids while flax seeds and wild sesame seeds contain about 60% of Omega-3 Fatty Acids and there’s about 20% of it in Hemp and Niger seeds, and seven percent in mustard and canola seeds.
Primary functions of Omega-3 Fatty Acids
The human body needs EFAs to form healthy cell membranes, proper functioning and development of the brain and nervous system and to repair cell membranes. A primary function of EFA is to produce hormone like substances called eicosanoids (thromboxanes, leukotrienes, and prostaglandins) which are signaling molecules and responsible for regulating blood pressure, blood viscosity, vasoconstriction, fertility, immune and inflammatory responses.
Omega-3 and Omega-6 fatty acids compete with each other for the production of their corresponding eicosanoids. Omega-6 eicosanoids are bad and cause inflammatory whereas Omega-3 eicosanoids have anti-inflammatory effects. So excess Omega-6 Fatty Acids interfere with the health benefits of Omega-3 Acids and there will be an increased risk of cardiovascular disease, obesity, rheumatoid arthritis, cancer, asthma, neurological disorders, diabetes etc. Omega-3 Fatty Acids are also highly concentrated in the brain of the human body and thus has a crucial role to play in proper brain functioning.
Symptoms of deficiency of Omega-3 Fatty Acids
Symptoms of Omega-3 Fatty Acids deficiency include fatigue, poor memory, dry scaly skin, insulin deficiency, inflammatory symptoms, obesity, non-alcoholic fatty liver, schizophrenia, mood swings or depression among others. Omega-6 Fatty Acids deficiency symptoms can include arthritis like condition, skin eruptions, slow wound healing, behavioral disturbances and heart and circulatory problems.
Recommendations for healthy life
Since Omega-3 Fatty Acids can’t be made in the human body, we have to incorporate it in our diet. A daily dose of three grams of Omega-3 Fatty Acids is considered to be safe and meets the requirements of the human body. Approximately, one to two tablespoon of mustard oil or minimum four grams of flax or wild sesame seeds in your daily diet can fulfill the minimum required dose of Omega-3 Fatty Acids. In case there’s a deficiency of Omega-3 Fatty Acids, fish oil supplements can help reduce the risk of chronic diseases. The strongest evidence for a beneficial effect of omega-3 fats has to do with heart disease. It is thus important to eat fish or other seafood at least one to two times per week, particularly fatty (dark meat) fish that are richer in EPA and DHA. This is also very important for pregnant women or those hoping to become nursing mothers in the future.
The author is a chief scientific officer at Nepal Academy of Science and Technology, NAST.
You May Like This

Keeping diabetes at bay
Diabetes is one of the most common chronic diseases affecting people globally. Some 425 million people are currently living with... Read More...



Just In
- CM Kandel requests Finance Minister Pun to put Karnali province in priority in upcoming budget
- Australia reduces TR visa age limit and duration as it implements stricter regulations for foreign students
- Govt aims to surpass Rs 10 trillion GDP mark in next five years
- Govt appoints 77 Liaison Officers for mountain climbing management for spring season
- EC decides to permit public vehicles to operate freely on day of by-election
- Fugitive arrested after 26 years
- Indian Potash Ltd secures contract to bring 30,000 tons of urea within 107 days
- CAN adds four players to squad for T20 series against West Indies 'A'












Leave A Comment